- Published on
Realtime Database vs Cloud Firestore
- Authors

- Name
- Shahzad Afridi
- @codewithafridi
The database is the main actor when it comes to dealing with data within an application. The development of any application to store data required a database and become a mandatory part of it. Firebase provides Cloud Firestore and Realtime Database. In this blog, we will see the difference between both. Once we explore the article we will have a better idea of choosing which database for storing the data is good.
Realtime Database
Realtime database is a low-latency solution and synced states across the client’s real-time. Data is stored in JSON structure and synchronized in real-time to every client connected to the database.
Cloud Firestore
Cloud Firestore is a new and modified database with advanced features such as faster queries, and indexes, and flexibility in scaling as much as data can scale. Cloud firestore is a document-model structure that syncs data for client and server-side development.

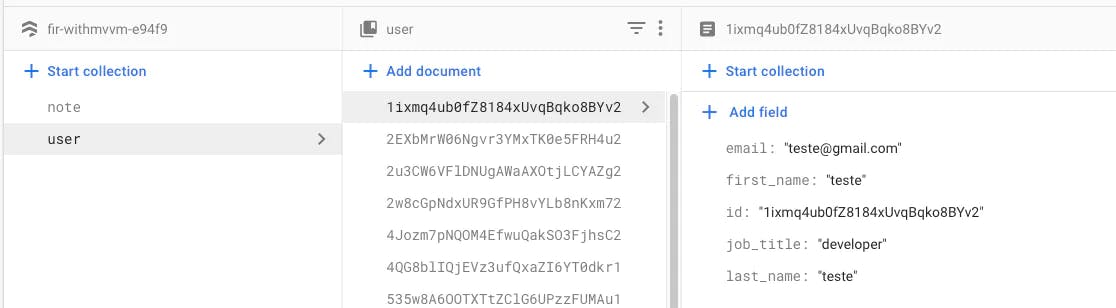
1. Querying and Structured data
Realtime Database :
- Realtime database is a giant JSON tree data structure. You can utilize deep queries with some limitations in sorting and filtering. If you want to filter data on a single property within a single query then you can't sort because both functionalities don't work in parallel so you will have to use one at a time.
- Realtime database has deep queries by default, so it returns the entire subtree.
- Realtime database doesn't have descending order query feature means If you want to fetch a record in descending order then you will have to do it manually.

Cloud Firestore :
- Cloud Firestore is a bit more structured than a Realtime database. Cloud Firestore is a document-model database, all the data is stored in objects called documents consisting of key-value pairs data structured. A document can also point to sub collection having more documents that point to other sub-collections, and so on. Cloud FireStore, You can use sorting, chain filters, and combine filtering on a property within a single query
- Structured data helps you use queries in a more efficient way meaning that you can fetch a document without getting all the documents and you can store data hierarchically in a way that makes it easier to understand logically without confusing yourself or worrying about the data.
- Cloud Firestore has shallow queries means these queries return documents in a particular collection or collection group. These queries don't return subcollection data.
- Cloud Firestore, has descending order query feature which helps to fetch records in descending order.
2. Manual fetching of data
Realtime Database :
- Realtime database is a real-time nature for building features like chat, location updates, or enabling collaborative experiences but many developers use the realtime database in a traditional way means Just fetching the data when I request it. Realtime database always listens to the data as new changes occur to the data then it triggers the listeners.
Cloud Firestore :
- Cloud Firestore is real-time in nature and simple one-time means you can request fetch data only one time. Of course, you can still add support for listeners, so that your client has the ability to receive updates whenever your data changes in the database. With Cloud Firebase you have the flexibility to retrieve the data however you want to.
3. Write and Transactions
Realtime Database :
- Realtime database, can execute a single operation as a query means you can execute an update to one node at a time, By updating another node you have to execute another operation as a query. You can write data through set or update.
Cloud Firestore :
- Cloud Firestore can execute multiple operations as a batch with any operator of the set(), update(), or delete() and complete all of them automatically. We can store arrays on firestore whereas Realtime database doesn't support the array
4. Scalability
Realtime Database :
- Realtime database is not automatically scaling. We have to customize scaling because it scales around 200k connections simultaneously and 1k writes per second in a single database. Realtime database gives you no limit on writes
- Realtime will be able to scale in a complex way which can cause confusion and worrying about the data. The more your database scale, the more effect on query performance because query performance is proportional to the size of your result set, not your data set. Searching will slow as your data is scaling.
Cloud Firestore :
- Cloud Firestore is automatically scaling. Firestore can accept up to 1 million connections simultaneously and 10k writes per second. There is a possibility that firebase can increase the limit in the future. Firestore has a limit on writes to every single document or index.
- Cloud Firestore will be able to scale better than the Realtime Database. As your database scales then it will not have any effect on query performance because query performance is proportional to the size of your result set, not your data set. So searching will remain fast no matter how large your data set might become. This means that a search for the top 10 restaurants in Chicago for a restaurant review app will take the same amount of time whether your database has 300 restaurants, 300 thousand, or 30 million.
5. Detecting presence
Realtime Database :
- The Realtime Database has native support for presence means it keeps track of client connection status and gives an update as client connection status changes.
Cloud Firestore :
- The Cloud Firestore doesn't support presence natively. You can use real-time database combinations to support presence, doing that you will need to explore cloud functions to sync Firestore and real-time database.
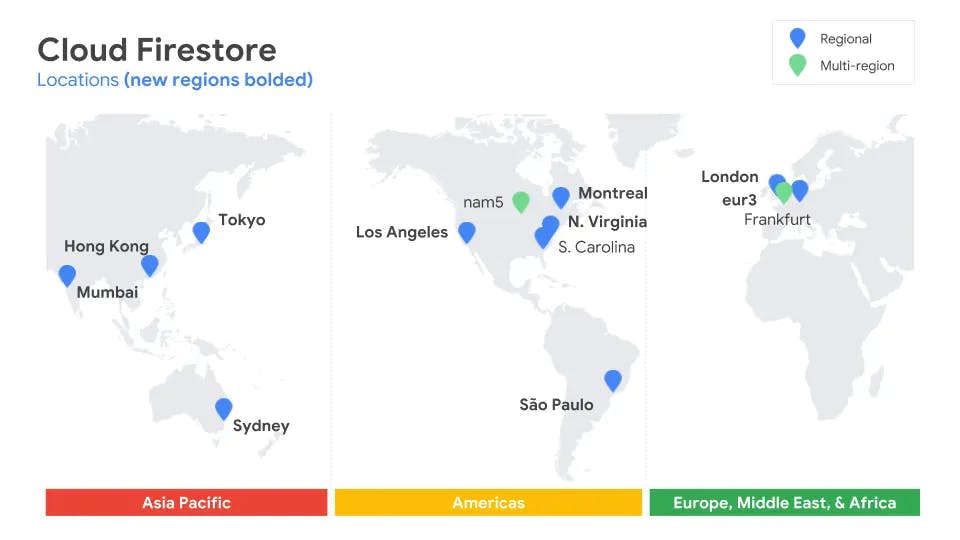
6. Multi-Region support for better reliability
Realtime Database :
- Realtime database has support for single-region locations. This means databases are limited to zonal availability. Extremely low latency is the ideal option for frequent state-syncing. If some unforeseen disaster were to render a data center then your data will goes offline and will not be able to continue to be served.
Cloud Firestore :
- Cloud Firestore has support for multi-region locations. This means that your data is automatically copied to multiple geographically separate regions at once. So if some unforeseen disaster were to render a data center — or even an entire region — offline, you can rest assured that your data will continue to be served
- And for you database aficionados out there, we should point out that Cloud Firestore offers strong consistency (just like Cloud Spanner!), which means that you get the benefits of multi-region support, while also knowing that you'll be getting the latest version of your data whenever you perform a read.
- There are currently two different multi-region locations you could use to host your data (one in North America, the other in Europe). And for those of you who don't need the heavy-duty capabilities of a multi-region database, Cloud Firestore also offers several regional instances in locations around the world, most of which will be available at a lower price tier starting in early March 2019. By contrast, the Realtime Database is only hosted in North America.
7. Security
Realtime Database :
- Realtime database, data validation does not happen automatically means validate data needs validate rules. Authorization and validation are handled separately but we can easily validate data by using validation rules
- Realtime database rules, reads, and writes from mobile SDKs secured.
Cloud Firestore :
- Cloud Firestore, data validation happens automatically means authorization and validations are combined. Read and write rules are secured by Firebase security rules. You can restrict the query to access specific collections or documents of data by specifying the rules in the security rules section. Cloud Firestore has more robust security for mobile, web, and servers than realtime databases.
- Cloud Firestore security rules, reads, and writes from server SDKs secured.
8. Offline Support
Realtime Database :
- Offline support for Android and iOS clients.
Cloud Firestore :
- Offline support for Android, iOS, and Web clients.
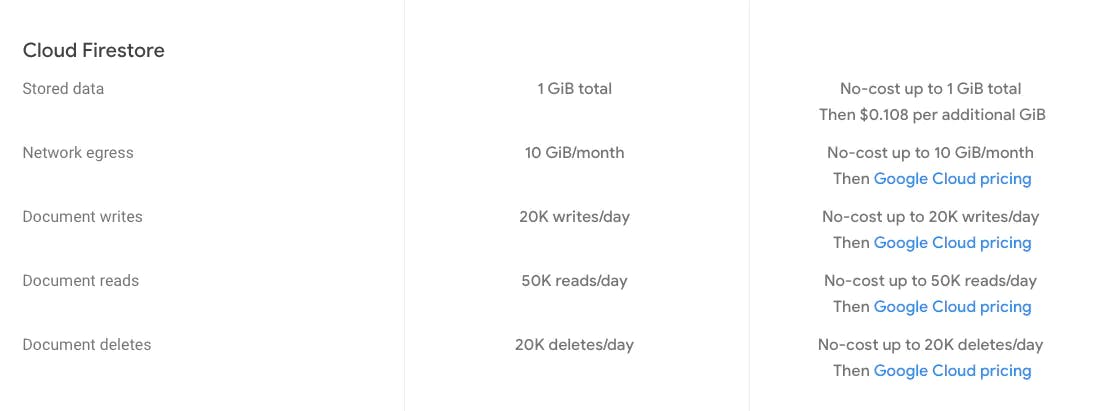
9. Different pricing model
Realtime Database :
- Realtime database, charges only for bandwidth and storage, but at a higher rate.

Cloud Firestore :
- Cloud Firestore charges depending on the operations such as read, write and delete at a lower rate, bandwidth, and storage e-g number of reads, write and delete operations performed on the data, amount of storage consumes by the database with indexes, and amount of network bandwidth
- Cloud Firestore charges on listening to the data means If your app listens to query data, and is charged for reading documents, the same applies to adding or updating. If you remove any document from the collection then it can also be charged because the listener gets triggered by the change that occurred in the query data.
- Cloud Firestore, charges are low as compared to Realtime Database.
Cloud Firestore does charge significantly_lower than what you would see in the Realtime Database.
What this means is that if you have a more traditional mobile app where your client is occasionally requesting larger chunks of data from your database — think something like a news app, a dating app, or a turn-based multiplayer game, for instance — you will find that Cloud Firestore's pricing model might be more favorable than if you run the same app on the Realtime Database.
On the other hand, if you have an app that's making very large numbers of reads and writes per second per client (for instance, a group whiteboarding app, where you might be broadcasting everybody's drawing updates to everybody else several times a second), Cloud Firestore will probably be more expensive. At least for that portion of your app — you can always use both databases together, and that's fine, too.
Of course, these are just rough guidelines, make sure you check out the Pricing section of our documentation for all the details on Cloud Firestore pricing.
Conclusion
As we go through all the points so we can conclude which one is better. I recommend Cloud Firestore over Realtime database because It gives you better performance, strong security, combined filters, indexing, and importantly It is scalable no matter how much your data scales.
There is another thing more I want to add If your application read/write requires a lot then I would consider a combination of Firestore and Realtime Database e-g I have to develop a delivery tracking app then I will keep locations-related data on Realtime Database as it updates every few seconds and other details info user, delivery and price, etc info will keep on firestore.
Firestore charges on reading/writing data so make sure you arrange data in a way that doesn't cost you much.
Other Important links:
https://firebase.blog/posts/2017/10/cloud-firestore-for-rtdb-developers
https://www.javatpoint.com/firebase-firestore-vs-realtime-database